ZEB Zero Energy Building
+
ZWB Zero Water Building
Scroll Down
Our vision for ZEBs
Zero energy building (ZEB), which has become a standard as the best form of green architecture, is now setting up those concepts of unifying architecture with nature and realizing a healthy living environment as its essential theme. One of the goals set by SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) is to make “clean water and sanitation” available throughout the world. Along with the effective use of water resources, zero water building (ZWB) is taking a growing interest. With engineers in the organization, Nikken Sekkei has, since its establishment, created energy-efficient and attractive green architecture based on sharing values with designers. Underlying this is our approach of providing healthy and comfortable building environments in the most efficient way, without tending towards technocentrism or blindly accepting fashionable designs. This kind of building environment is also our vision for zero energy buildings.
CATEGORY
Shifting from ZEB to Biophilic Design
Timeline for green architecture
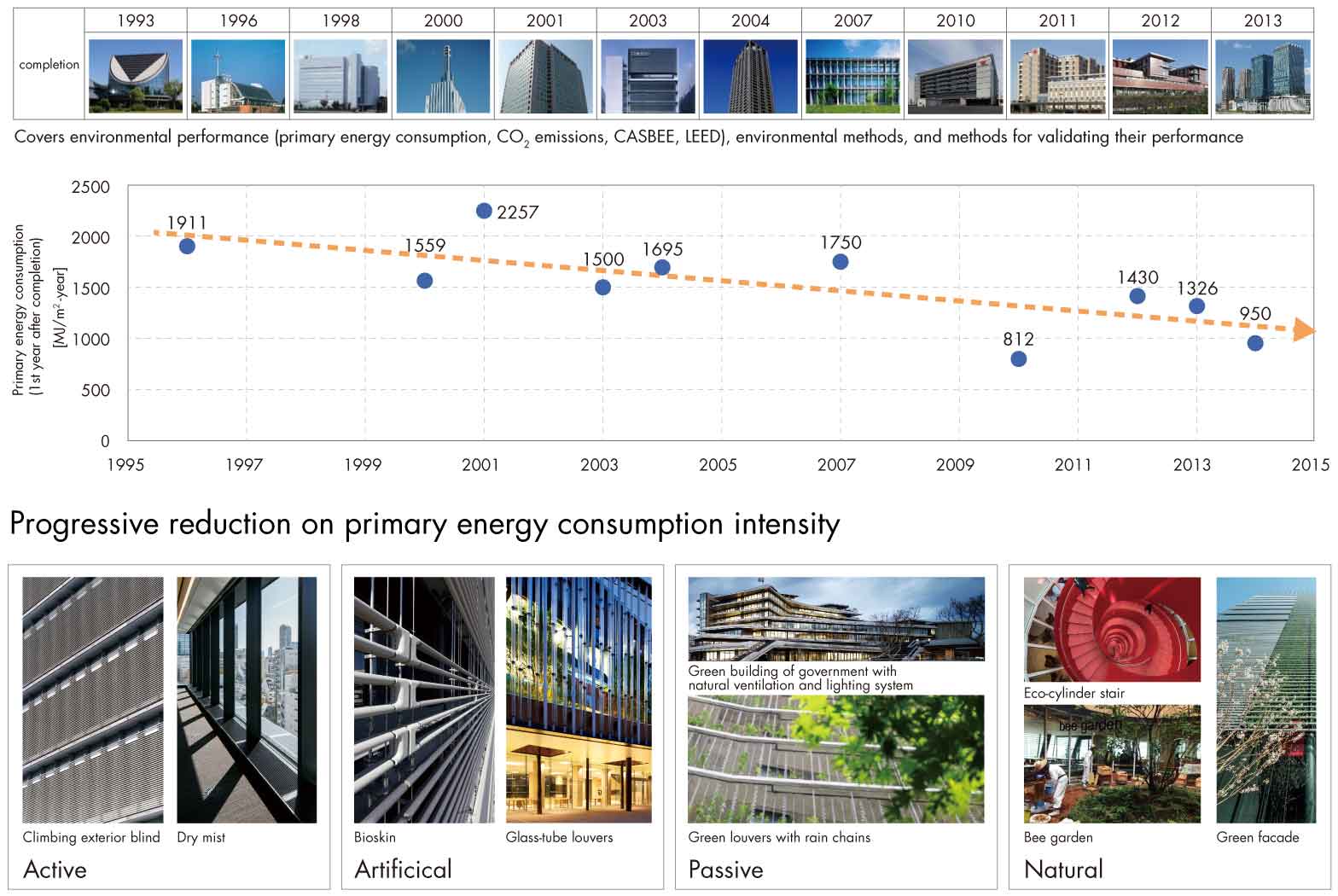
Not only Japan, but also in the United States, the United Kingdom and other countries set up ambitious realization targets of ZEB for the timeframe from 2020 to 2030. It is necessary to further promote energy saving, and how we should introduce renewable energy use.
It will be asked for ZEB not to get radicalized of its idea and theme by relying solely on technology and theories, but to provide an architectural environment for occupants to live in a healthy, comfortable and rich lifestyle. Green architecture has been developed in diverse directions in active or passive methods, or in combination of both, while either method suggests ingenious application of natural principles utilizing light, wind, greenery, or evaporation and shielding.
As shown in the above example figure, smartly designed architectures bring in natural environment into architectural environment, along with external blinds and biological skins to bring in natural light while blocking solar radiation heat, glass-piped louvers to bring in light beautifully, the facade highly integrating exterior wall with green wall system, a bee garden inside the building, and spiral staircase named “ecological cylinder,” in which curves found in nature are applied. ZEB is truly transforming its way into a style called biophilic design oriented toward integration of architecture with living organism and nature.
ZWB, as Crucial Element of SDGs
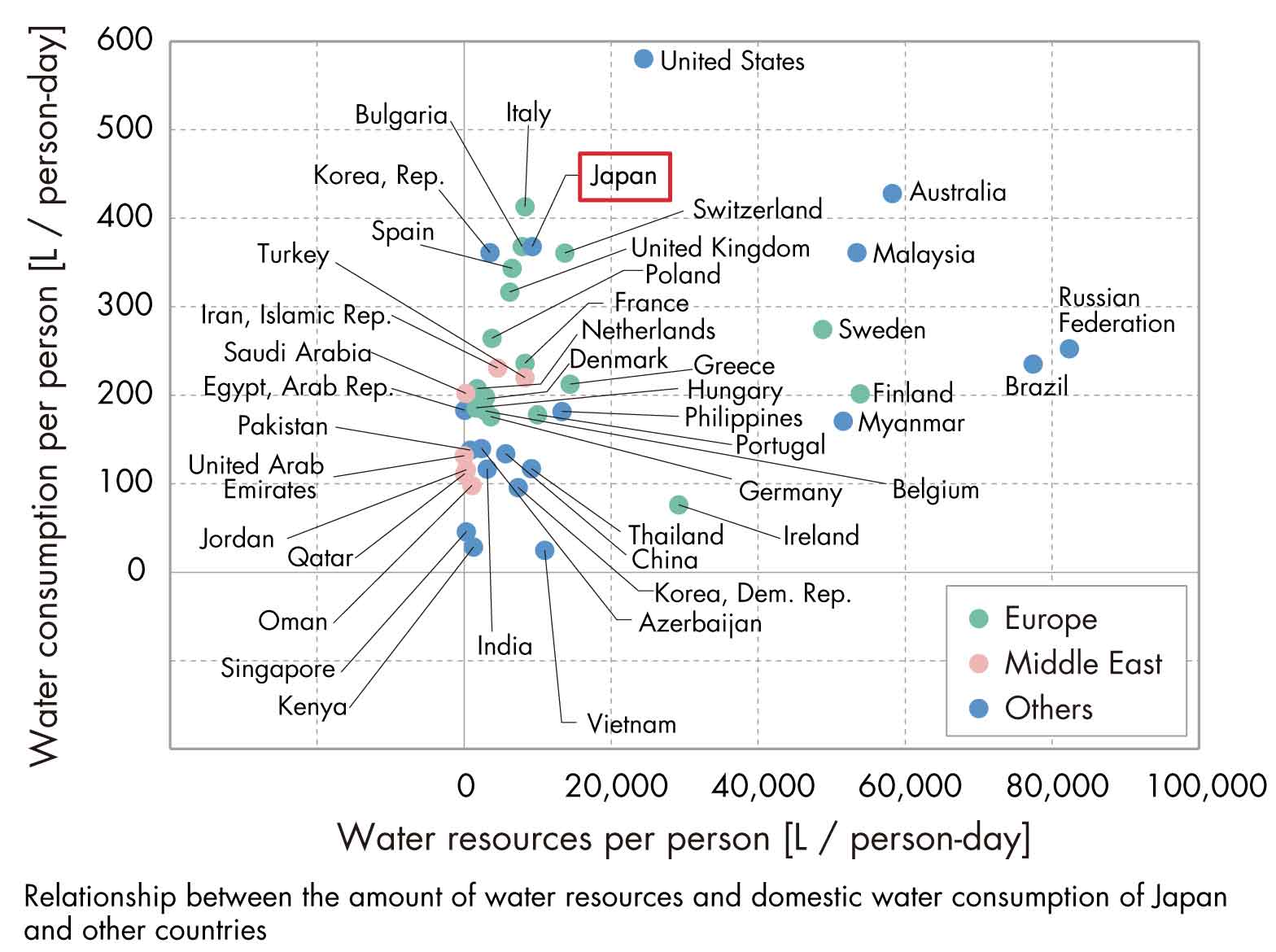
Throughout the countries in the world, various developments for the effective usage of water resource has been in progress mainly around drought area where the value of water is high. Shown here are the actual examples of advanced water utilization; for example, an office building which collects water sprinkled for evaporative cooling and reuses it for radiative cooling inside of its interior space, and a water reclaiming system, “sewer mining,” which considers sewer as the “mineral vein” for water resource and bring back sewage water into the building for recycled usage.
In this article, ZEB and ZWB is mentioned not only to suggest synergistic effect of energy saving and water saving, but also as an integral element composing green architecture, contributing to the realization of the healthy living environment integrated with nature.
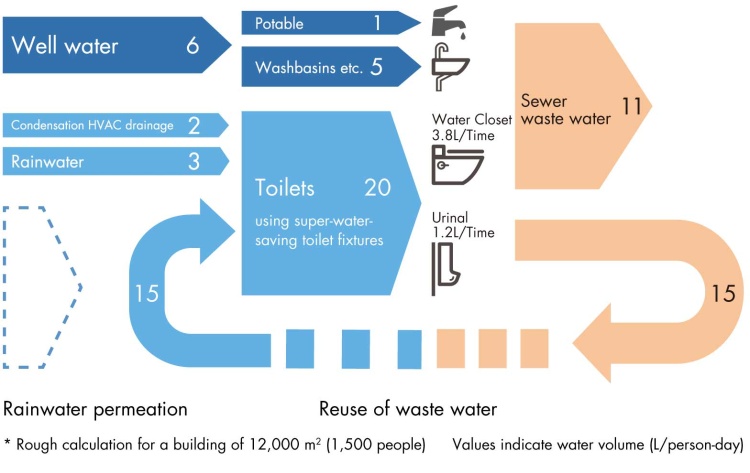 Water balance of zero water building
Water balance of zero water building
Water balance is calculated for a zero water building not relying on portable water supply infrastructure. By using data of latest equipment with water saving feature for its water consumption, the feasibility of a zero water building is examined combining waste water treatment system with recycled water from humidifier condensation, HVAC drainage, well water and rainwater
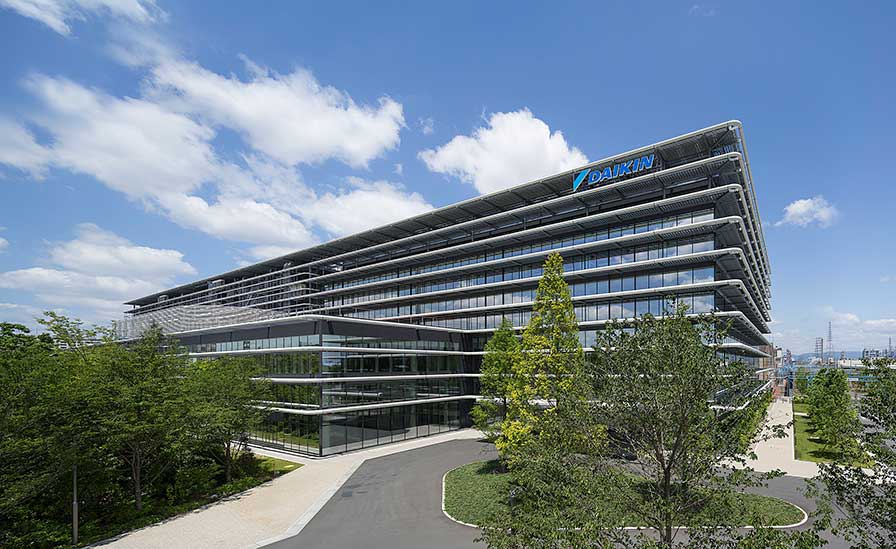
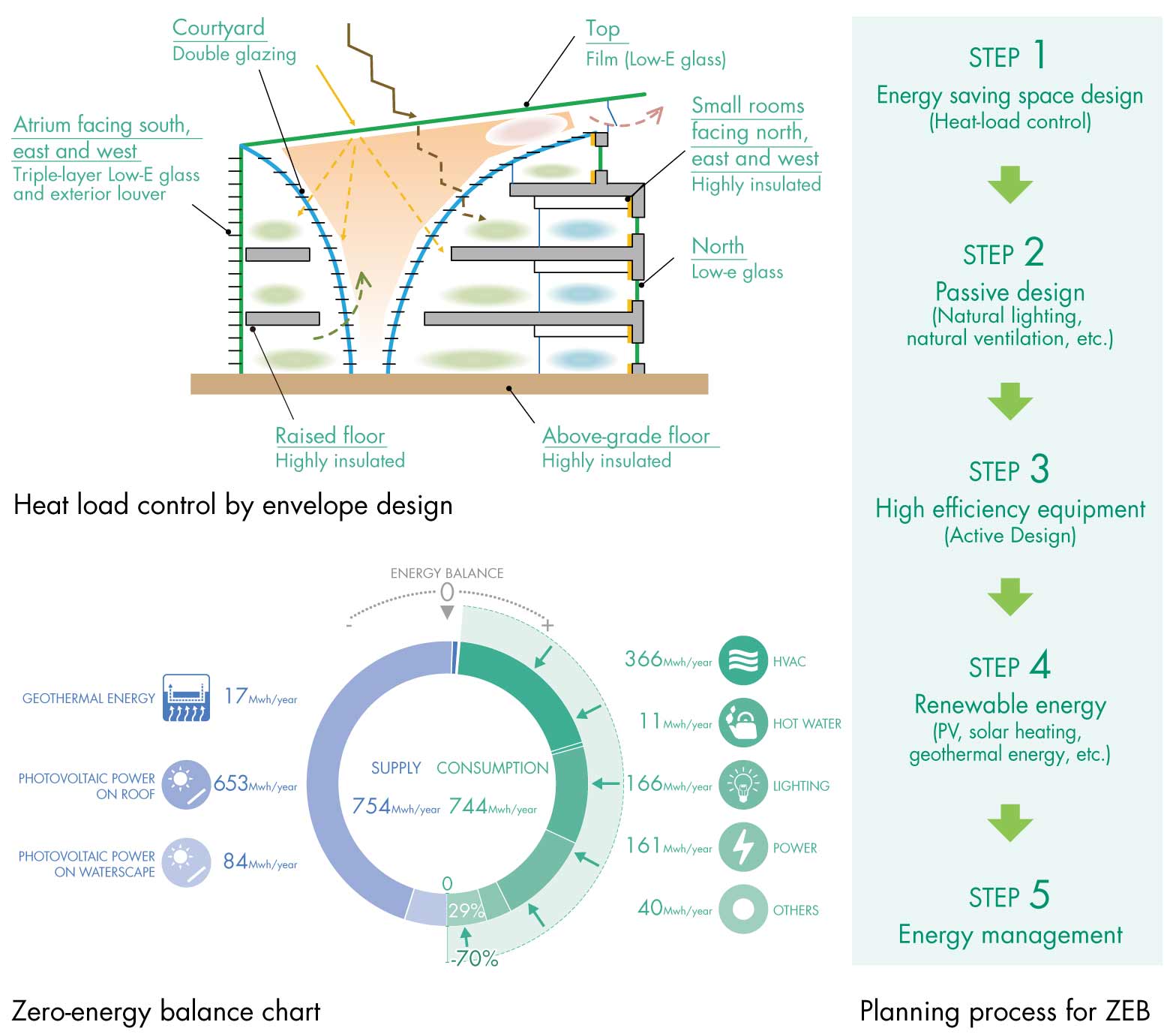
 DAIKIN Technology and Innovation Center
DAIKIN Technology and Innovation Center
<Related article>DAIKIN Technology and Innovation Center

Smart ZEB Approaching from Envelope Design
>Enlarge the image
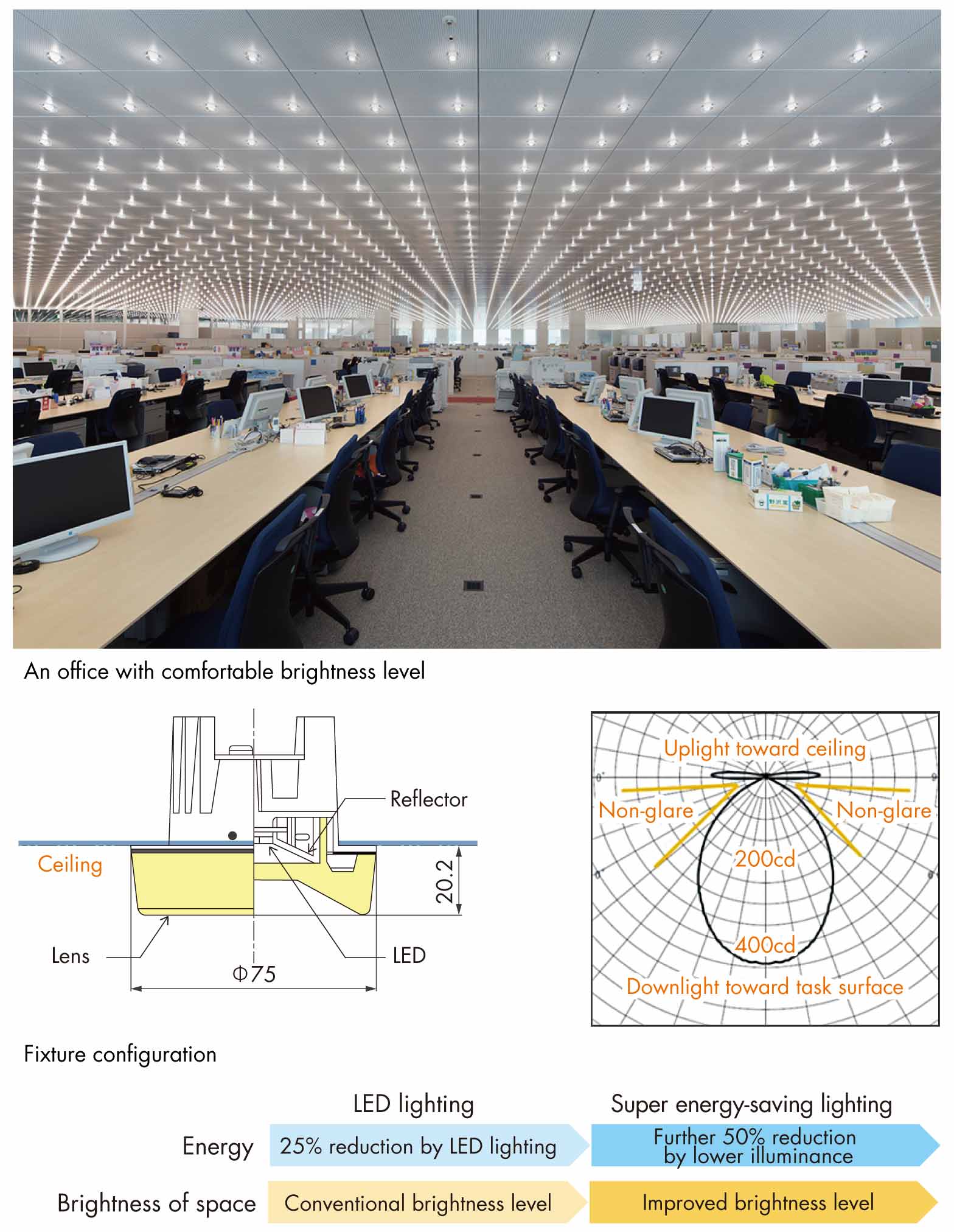
Super Energy Saving Lighting Equipment That Maintains Luminance
>Enlarge the image
Energy Saving, Comfortable Radiant Cooling with Laminar Flow
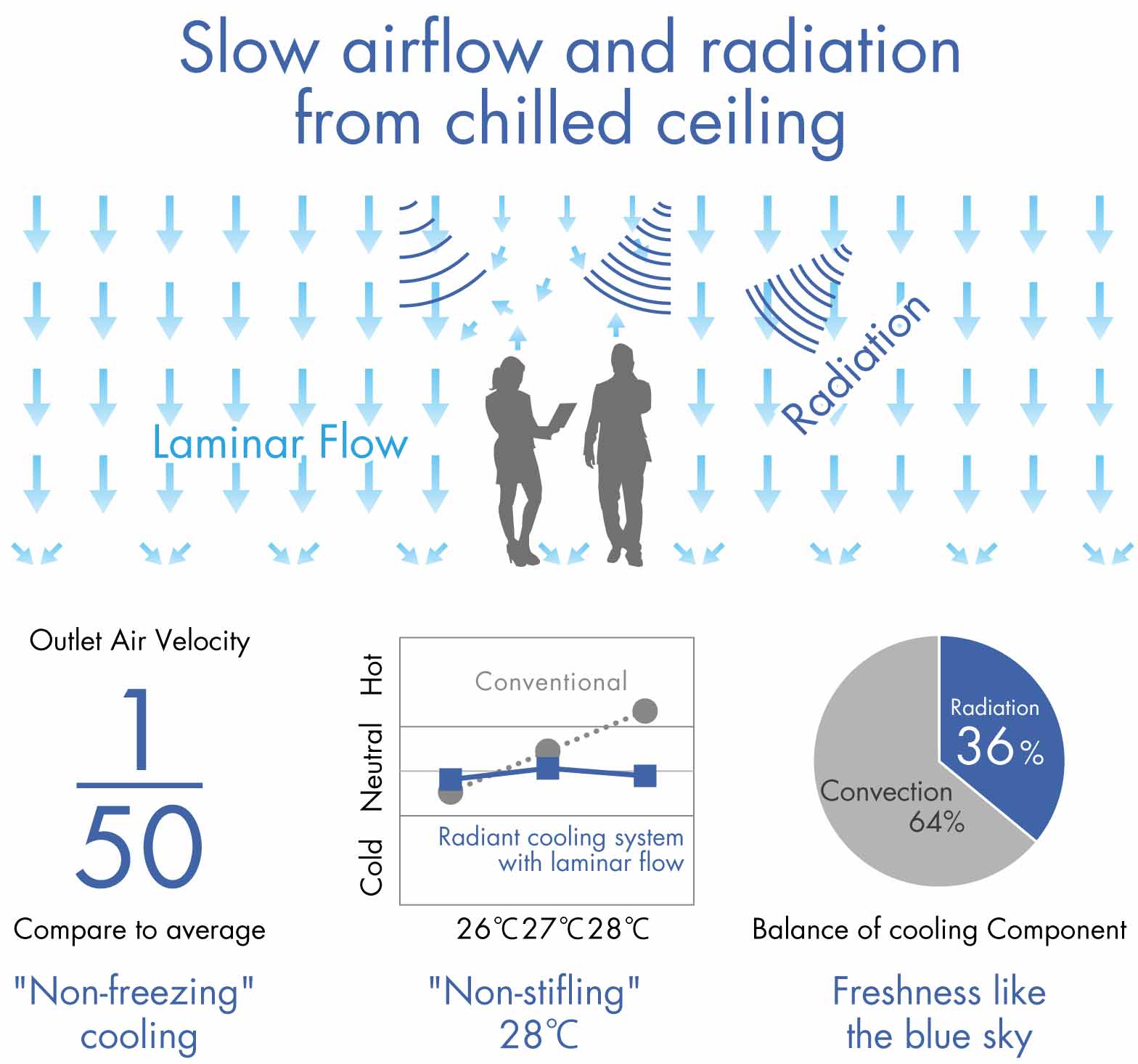
>Enlarge the image
A Natural Ventilation Design Tool using Existing Examples
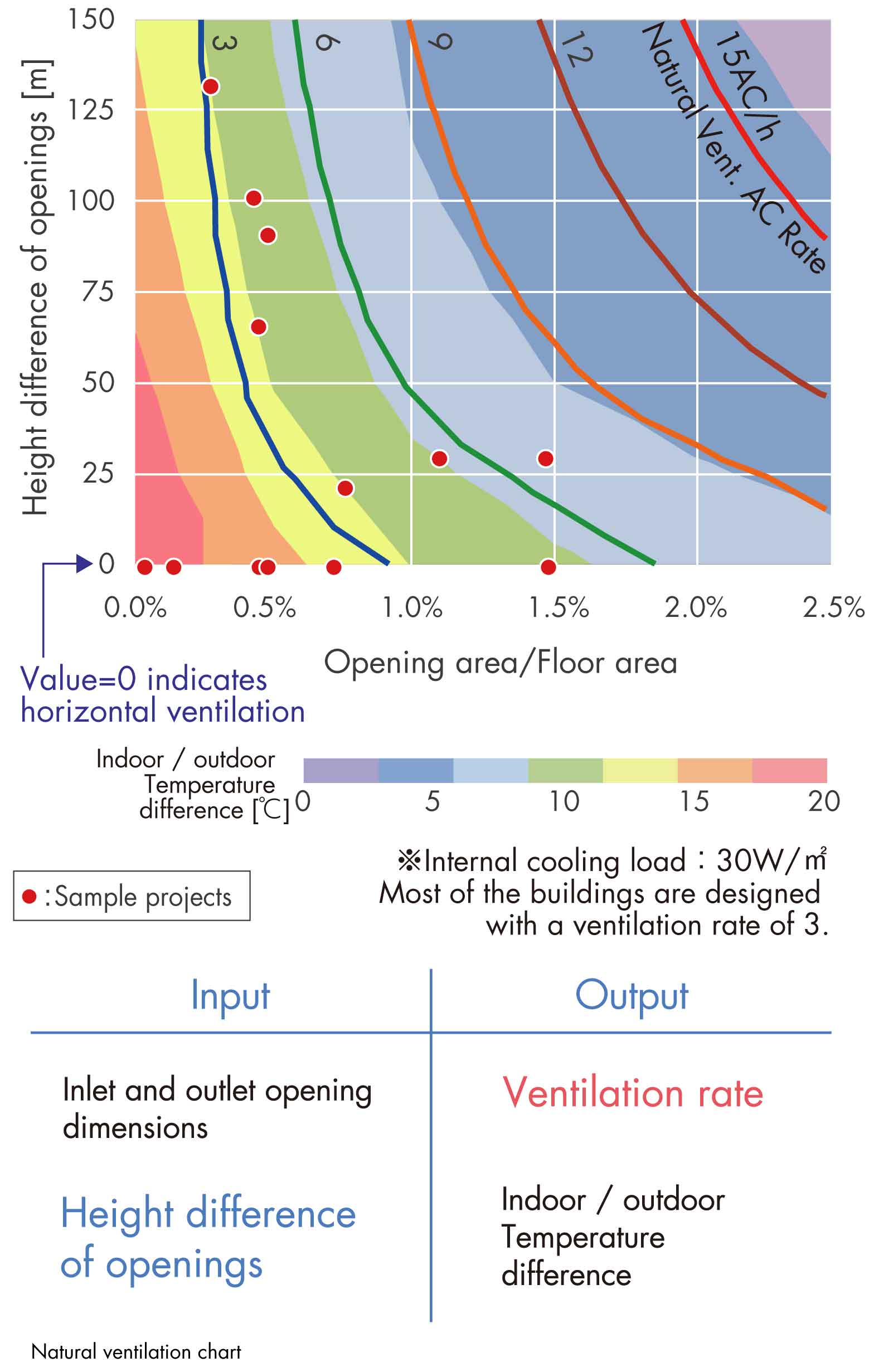
>Enlarge the image
Cool Down Outdoor Air with Dry Water Mist
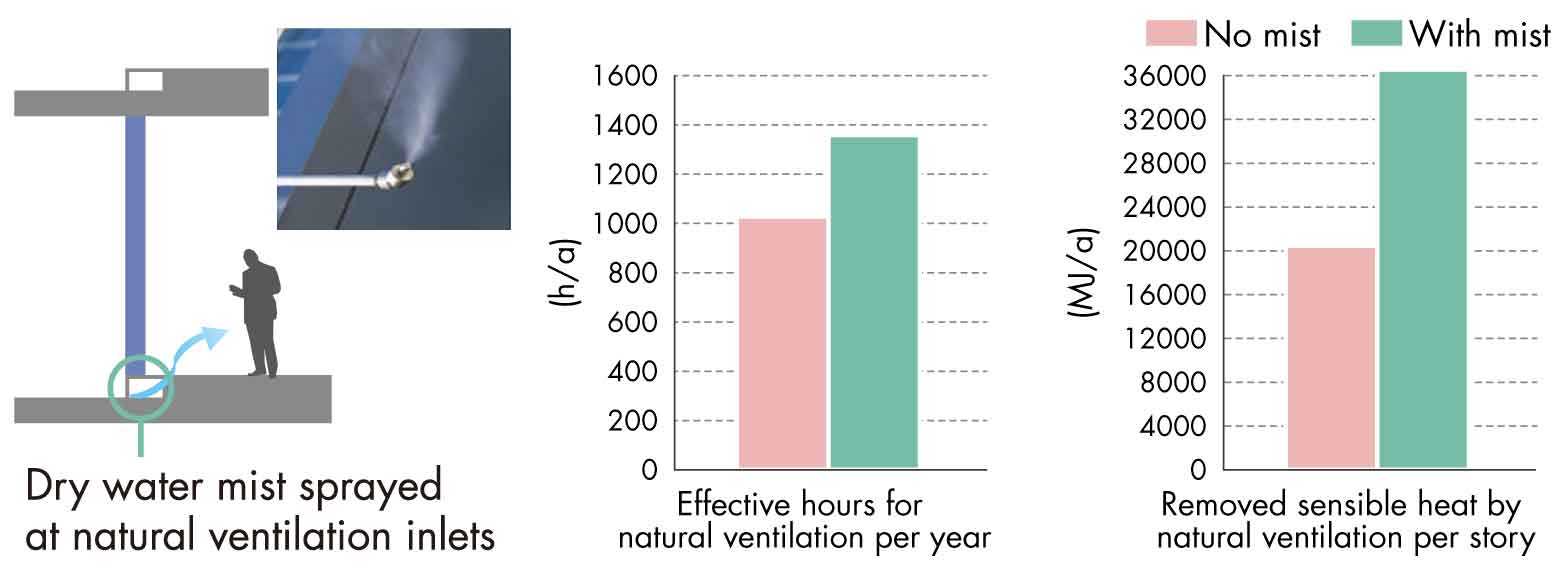
>Enlarge the image
Studying Dramatically Accelerating Energy Saving Policy in China
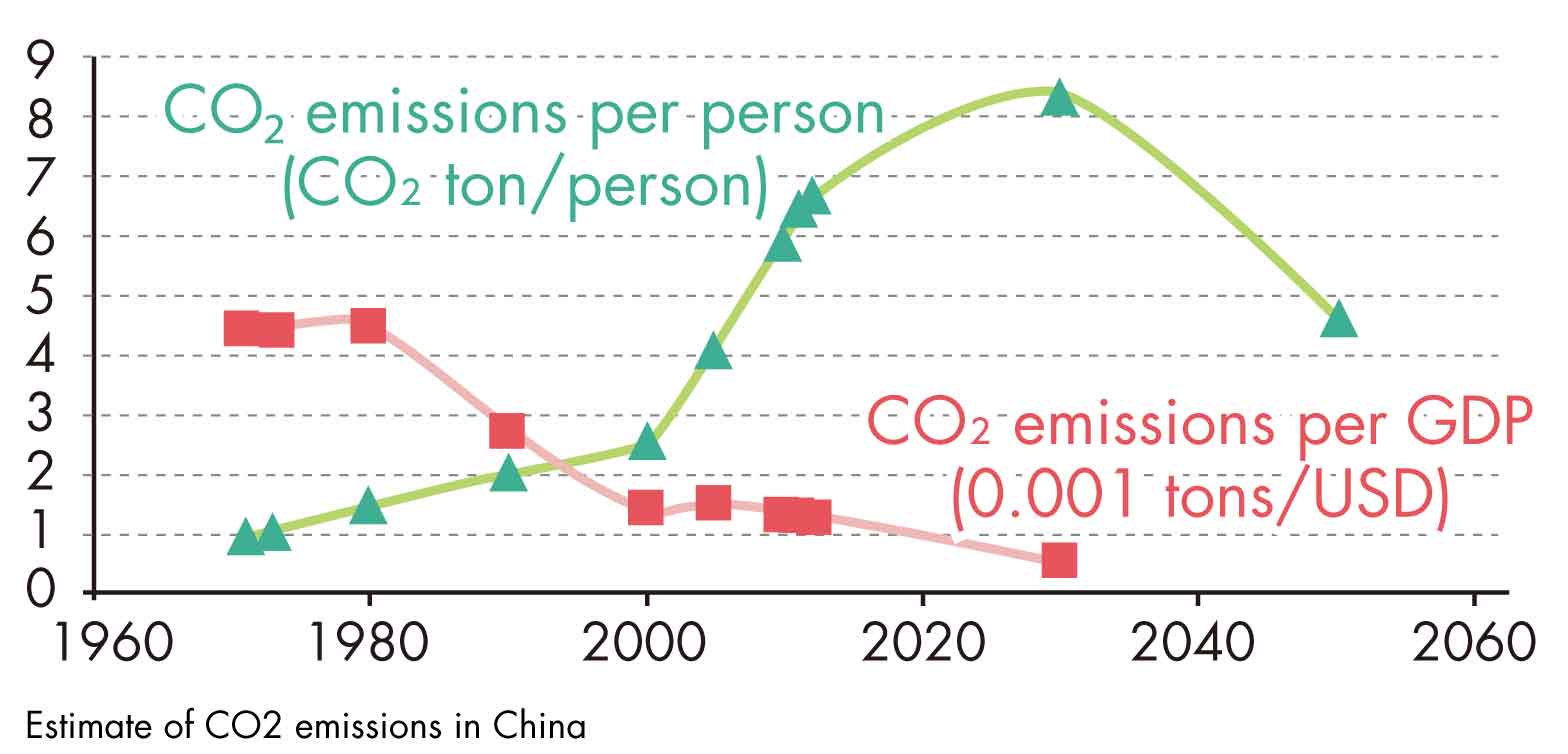
>Enlarge the image
ZWB Proposal Considering the Situation of Water by Countries
>Enlarge the image
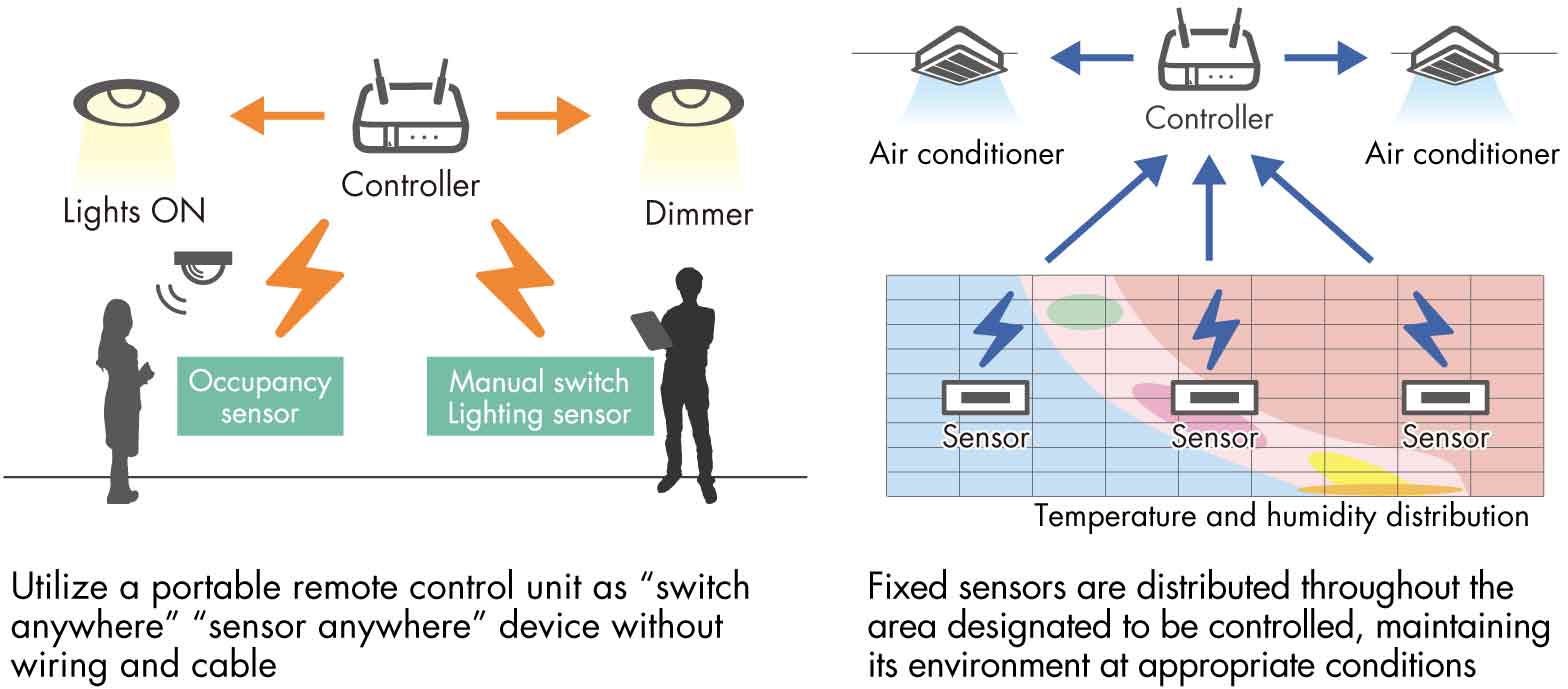
Energy Harvesting Technology to Support ZEB
>Enlarge the image